Expansionary Monetary Policy | A-Level Economics Model Paragraph (AQA, Edexcel, OCR)
Monetary policy is the use of interest rates to influence the aggregate demand and therefore the inflation rate of an economy. Expansionary monetary policy involves the reduction of interest rates by the Bank of England. This means there is a lower cost of borrowing and lower reward for saving. This means that consumer spending and investment is likely to increase so therefore aggregate demand will shift to the right from AD1 to AD2, since AD = C + I + G + (X-M).
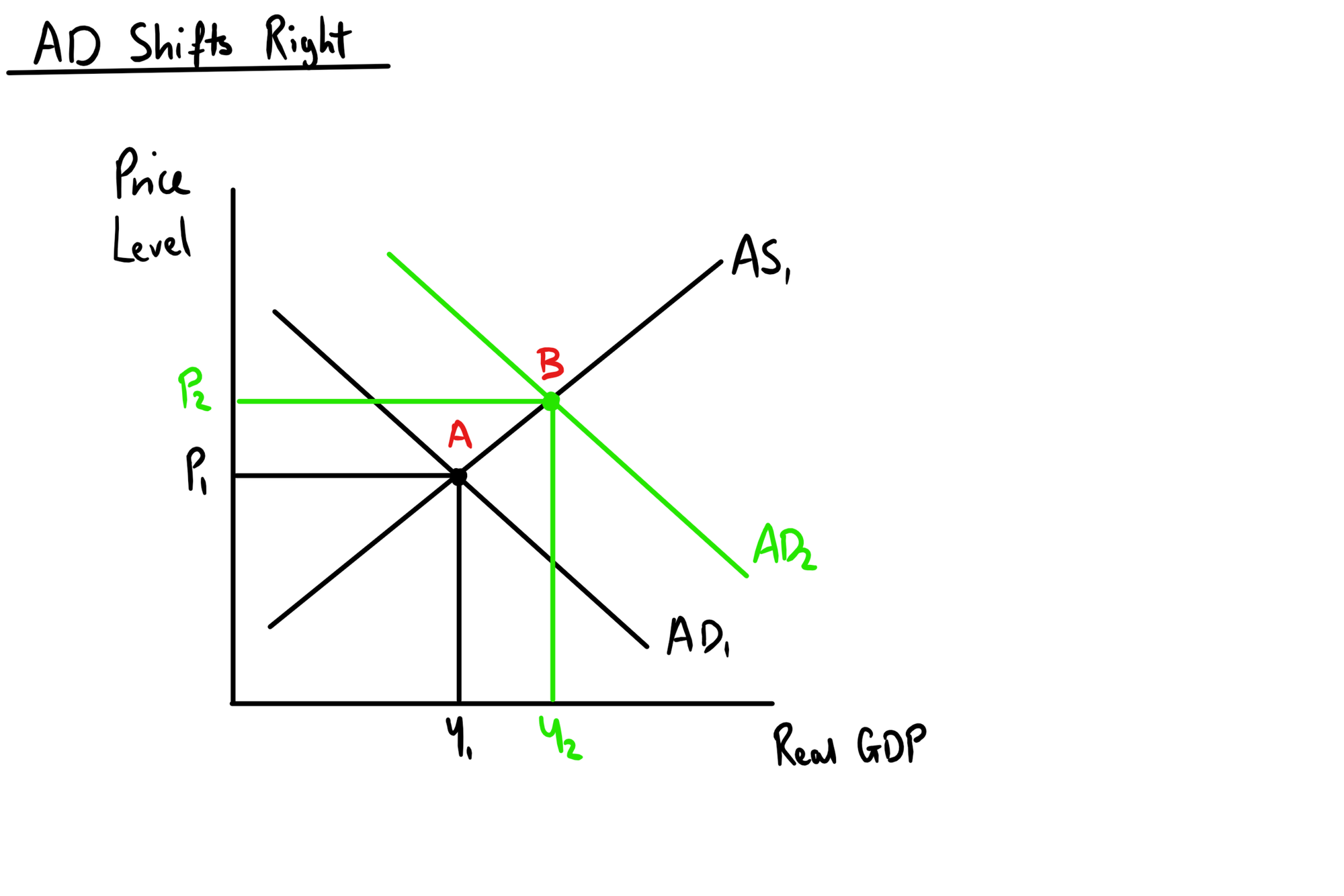
The diagram shows that there is an increase in output (real GDP) from y1 to y2 - so there is economic growth. This means that there would also be a decrease in unemployment because there is greater production of goods and services which means there would be a greater demand for workers. Also, price level increases from PL1 to PL2 which means there is an increase in the rate of inflation. This iis due to the greater demand for goods and services which adds pressure on to businesses. Therefore, expansionary monetary policy can be used to achieve economic growth, lower unemployment, and a higher rate of inflation.
Monetarists argue that increasing money supply is by far the most effective way to increase price level. This is because of their understanding of the Fisher equation - MV = PQ. They assume that real GDP (Q) and the velocity of money (V) are always constant, which means that money supply (M) directly affects price level (P).
However, Keynesian economists argued against these assumptions - they believe that V and Q can change and have a significant impact on price level. Depending on the state of the economy, monetary policy may be ineffective. For example, if aggregate demand is very low and there are low levels of confidence in the economy, then a reduction in interest rates is still unlikely to encourage borrowing and discourage saving. People may be saving money during a recession as they are worried about losing their jobs or having a lower income - so there would be a low circulation of money and a low demand for goods and services. Therefore, people will not suddenly choose to borrow and spend money purely because of a small fall in interest rates. This is also known as a liquidity trap.