Supply side policies are the range of policies that can be used to increase the productive capacity of the economy. There are both interventionist and market-based supply-side policies. One example of an interventionist policy is an increase in spending on infrastructure, for example with HS2. This increase in spending would aim to cause an improvement in transport links around the UK which would allow businesses to increase their productivity (output per worker or output per hour). As a result, businesses around the UK would be able to produce more goods and services with the same amount of resources. The impact of this is a right shift in long run aggregate supply.
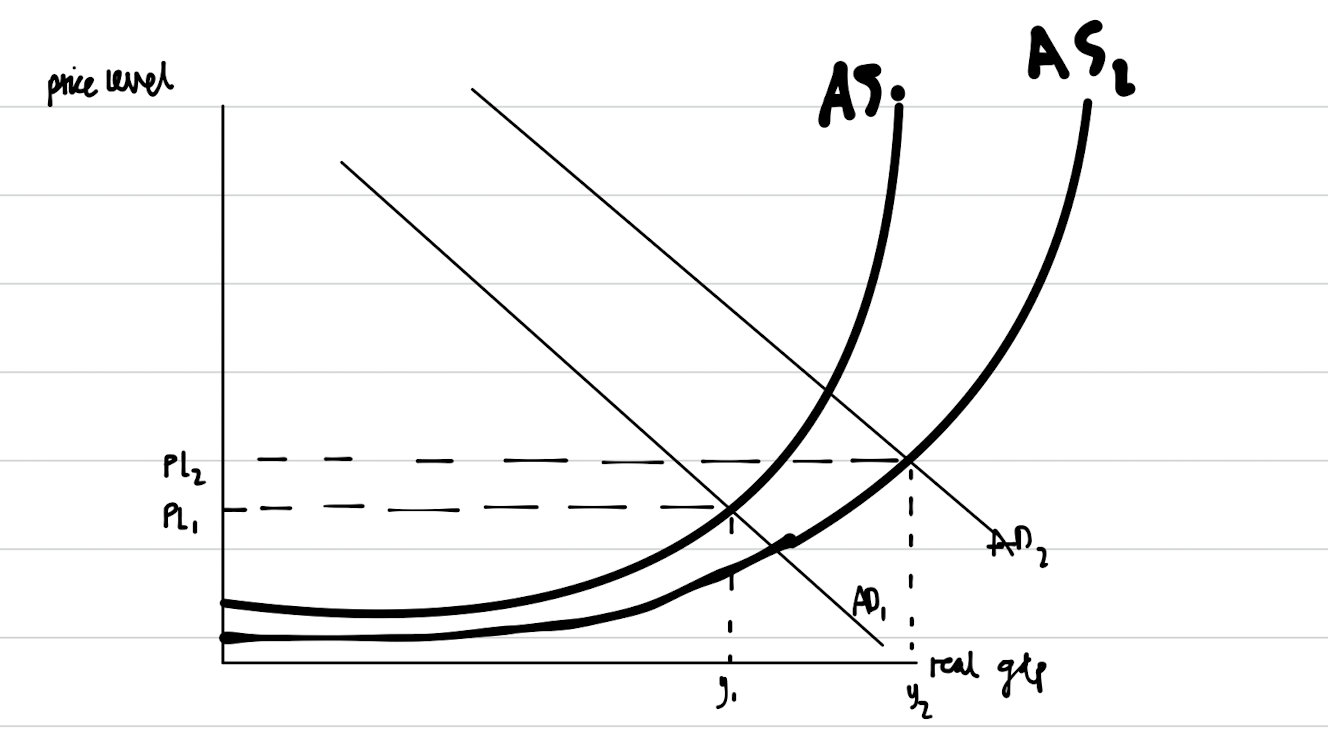
As a result, there would be an increase in economic growth due to the increase in real gdp produced by firms, and a decrease in unemployment. There would also be a fall in price level as there is less pressure on existing factors of production.
However, the issue with supply-side policies is often the substantial opportunity cost as well as the time lag. For example, the total budget for HS2 could reach close to £100 billion by completion. Also, the plans were proposed in 2010 but parts of it won't be completed until around 2040. Therefore, we wouldn't see the impact on the economy until then.
But overall, in the long run, supply side policies are the best and only way to achieve all four macroeconomic objectives without causing conflict.