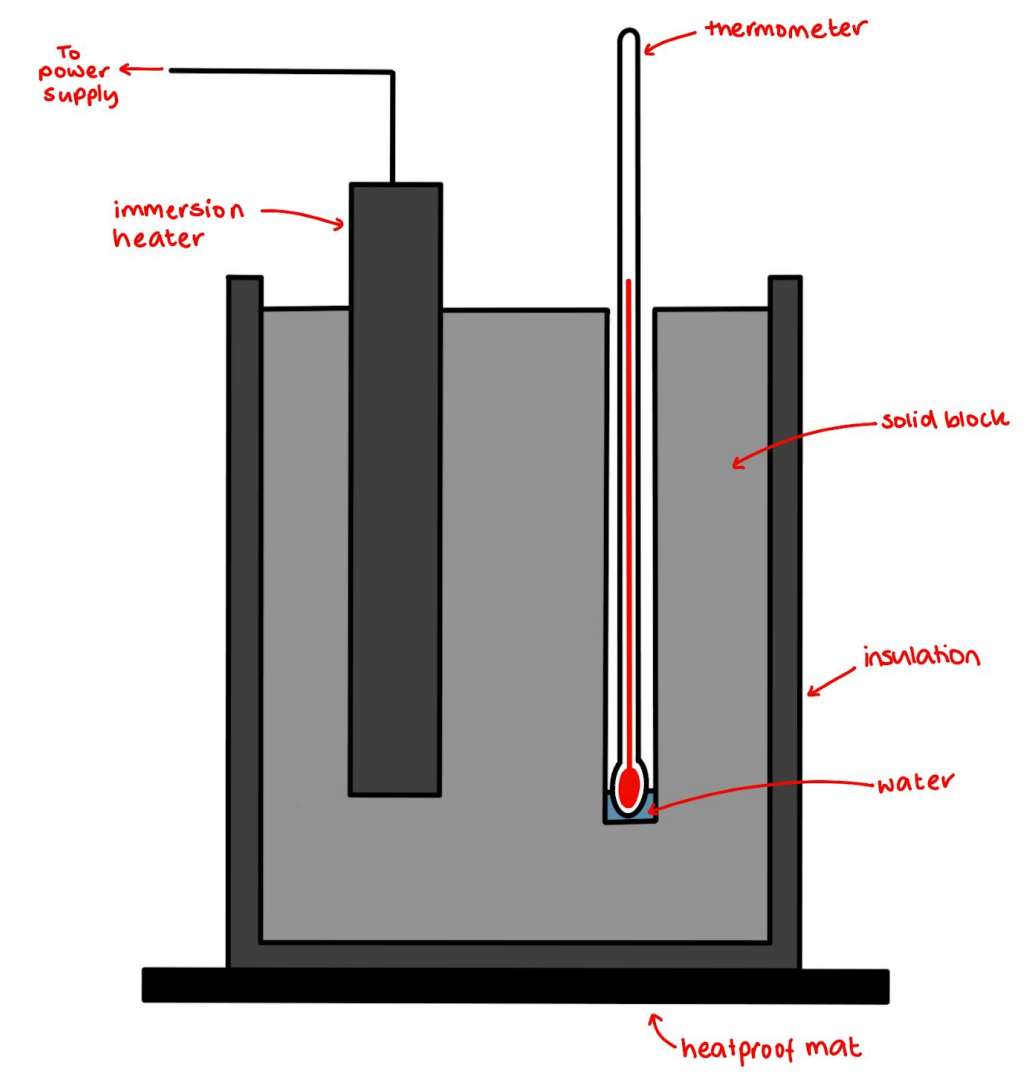
Required practical activity 1:
If you want to determine the specific heat capacity of a material:
- get 1kg of your material and insulate.
- place on heat proof mat and have thermometer, heater (12V) and power supply (30W) ready.
- measure the initial temperature and turn the power supply on.
- measure the temperature and power (using P=IV) every 10 minutes for 30 minutes.
- work out the energy (E=P/t).
- work out specific heat capacity using Q = m x c x T
Safety and Improvements:
- insulate every side properly
- heat proof mat and goggles
- careful of spillages
- let equipment cool down, do not touch
Required practical activity 2:
if you want to test which thermal insulators work best
- set up equipment (kettle water, thermometer, different insulating materials or factors e.g. newspaper, cotton, different sized beakers)
- wrap each beaker with material including the top (leave space to add water and thermometer)
- add kettle water to each beaker which are all different
- measure temperature every 3 minutes
- calculate temperature (new temperature - old temperature)
Required practical activity 3:
use circuit diagrams to set up and check appropriate circuits to investigate the factors affecting the resistance of electrical circuits. This should include:
• the length of a wire at constant temperature
• combinations of resistors in series and parallel.
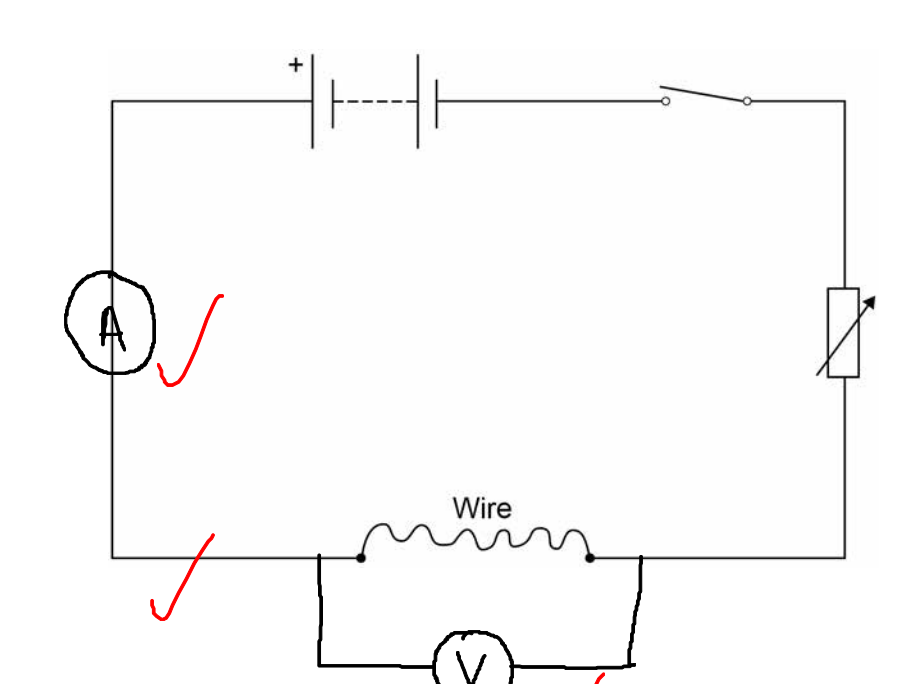
- use a ruler to measure the length of the wire
- use an ammeter in series to measure the current through the wire
- use a voltmeter in parallel to measure the potential difference across the wire
- use R = V/I to measure the resistance
- repeat three times and remove outliers and take an average for reliability
- change the length of the wire and repeat previous steps
- see if there is a trend when you change the length of the wire
- control variables: material of the wire
- independent variables: length of the wire
- dependent variables: voltage, current, resistance (because R=V/I)
- safety: use low current to prevent burns