- Ions: charged particles e.g. 1+ ion has lost one electron
- Ionic bonding is between metals and non-metals. Electrons are given and taken.
- Ionic bonding: electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions.
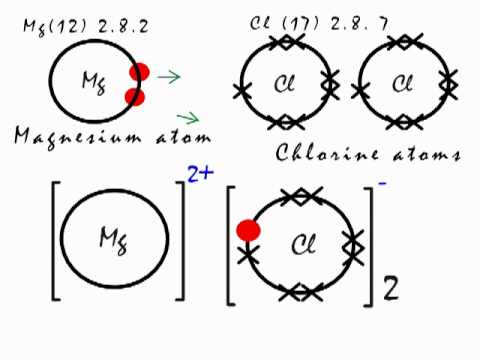
- Explain the bonding in magnesium chloride (3 marks): Magnesium chloride is formed when magnesium loses two elections and forms a 2+ ion, and each chlorine gains an electron and forms two 1- ions.
- Mg is a 2+. Cl is a 1-. Cross the numbers to form MgCl2.
- Na is a 1+. O is a 2-. Cross the numbers to form Na2O.
- Covalent bonding is between two non-metals.
- Covalent bonding: a shared pair of electrons between two atoms.
- Make sure each shell has 8 electrons
- Diatomic molecules exist as pairs (covalent) e.g. H2. They end in -gen including all halogens.
- Metallic bonding: electrostatic attraction between delocalised electrons (negative) and metal ions (positive).
Ionic Bonding Properties (Metal + Non-Metal)
- High melting point and boiling point due to strong electrostatic forces of attraction which require a lot of energy to overcome.
- Conducts electricity when molten as ions are free to move and carry charge.
- Doesn't conduct electricity when solid as ions are not free to move and carry charge.
Simple Covalent Molecule Properties (Non-Metals)
- Low melting point and boiling point due to weak intermolecular forces which require low energy to overcome.
- Doesn't conduct electricity as electrons are not free to move and carry charge.
Giant Covalent Molecules Properties (Graphite, Graphene, Diamond)
- High melting point and boiling point due to lots of strong covalent bonds which require a lot of energy to overcome.
- Doesn't conduct electricity as electrons are not free to move and carry charge (except for graphite and graphene).
- Diamond: each carbon is bonded to 4 other carbon atoms.
- Graphite: each carbon is bonded to 3 other carbon atoms.
- Graphene: a single layer of graphite.
- Sillicon dioxide: S02
- Fullerenes: hollow shapes made from carbon
- Buckminster fullerene: C60 was the first fullerene (shpere shape).
- Carbon nanotubes: very long cylinder fullerenes, useful for nanotechnology.
- Differences in properties: graphite is more slippery because there are weak intermolecular forces between layers so they can slide. Diamond can't conduct electricity but graphite and graphene can because there are free electrons.
Metallic Bonding Properties (metals on their own)
- High melting point and boiling point due to strong electrostatic attraction which requires a lot of energy to overcome.
- Conducts electricity as electrons are free to move and carry charge.
- Malleable (can be bent) as the layers can slide if you hammer it.
- Alloys are a mixture of two or more metals. They are stronger than pure metals because the particles are different sizes so they are not in neat rows and columns so they cannot slide easily if they are hammered.
- The three states of matter are solids, liquids and gases.
- States of matter: (s), (l) and (g), (aq).
- Changes of state: melting, evaporating, condensation, freezing.
- The energy needed to melt/ boil etc. (melting and boiling point) depends on the strength of the forces between the particles of the substance.
- Polymers: very large molecules and the atom are joined with strong covalent bonds so they have high melting points (they are solids at room temperature).
Triple Science Only
- Nanoscience: structures that are 1–100 nanometres.
- Fine particles (PM2.5): structures that are 100-2500 nanometres.
- Coarse particles (PM10): diameter between 1 x 10-5 and 2.5 x 10-6 metres.
- When the length in a cube x10, the surface area: volume ratio increases by x10.
- Nanoparticles have a high surface area to volume ratio so they have different properties.
- Uses: medicine, electronics, cosmetics and sun creams, deodorants, and as catalysts.