- Total revenue: price x quantity
- You can find it on the demand and supply graph. The area until equilibrium.
- Average revenue: total revenue/ quantity = price
- Marginal revenue: additional revenue from the next item sold
- When demand is price inelastic, you can raise prices and total revenue will not decrease.
- When demand is price elastic, firms can raise prices but total revenue will fall.
- Total cost: total fixed cost +total variable cost
- Total fixed cost: costs that do not vary with output e.g. rent
- Total variable cost: costs that do vary with output e.g. ingredients
- Average (total) cost: total cost divided by output
- Average fixed cost: fixed cost divided by output
- Average variable cost: variable cost divided by output
- Marginal cost: the extra cost of producing one extra unit.
- Diminishing marginal productivity: when you hire more workers, each worker slows down because they are sharing the same fixed factors e.g. 5 chefs in the same kitchen.
- Short-run: when there is at least one fixed factor of production.
- Long-run: when all factors are variable.
- Average cost curve: U-shaped
- Marginal cost curve: tick shaped
- Average revenue: downward sloping (demand curve)
- Marginal revenue: twice as steep as the AR curve.
- Economies of scale: when long-run average costs fall as output increases.
- Really Fun Mums Try Making Pies
- Risk (new recipe)
- Financial (access to finance)
- Marketing (every little helps)
- Technical (self checkouts)
- Managerial (easier to delegate work)
- Purchasing (bulk-buying)
- Diseconomies of scale: when long run average costs rise as output increases.
- coordination (difficult to manage the staff)
- control (difficult to identify weak spot)
- communication (workers feel alienated)
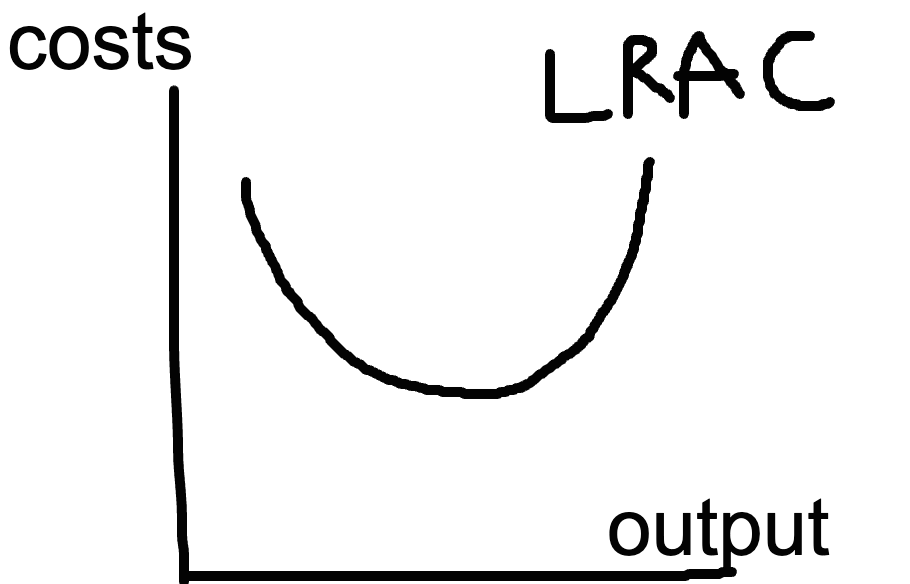
- Minimum efficient scale: the minimum level when a firm can first start to exploit maximum economies of scale.
- Internal economies of scale: affect one firm.
- External economies of scale: affect the entire industry.
- transport
- education and training
- infrastructure
- Profit maximisation: MC = MR
- Short-run shutdown points: when AC>AR