- Mean rate of reaction = amount of reactant used/ time taken = amount of product formed/ time taken
- Exact rate of reaction: draw a tangent and work out gradient
- Rate of reaction slows down over time. 1/t is proportional to rate of reaction.
- Factors affecting rate of reaction: concentration, pressure, surface area of the reactants, temperature, catalysts.
- Apart from catalysts, they all increase frequency of collisions and the chance of successful collision.
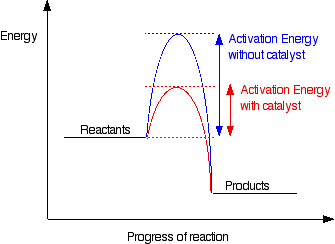
- Catalysts: provide an alternative reaction pathway with a lower activation energy
- Enzymes: biological catalysts.
- Reactions may be reversed (⇌) by altering the reaction conditions.
- Dynamic equilibrium: occurs in a closed system when the rates of forward and reverse reactions are equal.
- Le Chaterlier's Principle: If a change is made to any of the conditions in equilibrium, then the system responds to counteract the change.
- Higher temperature: equilibrium moves to the endothermic side
- Lower temperature: equilibrium moves to the exothermic side
- Higher concentration of reactants: equilibrium moves to the right
- Lower concentration of reactants: equilibrium moves to the left
- Higher concentration of products: equilibrium moves to the left
- Lower concentration of products: equilibrium moves to the right
- Higher pressure: equilibrium moves to the side with less moles of gas (count big numbers and count gas only).
- Lower pressure: equilibrium moves to the side with more moles of gas
Separate Sciences Only
- Concentration (mol/dm3) = Moles/ Volume (dm3)
- 1 dm3 = 1000 cm3
- Percentage yield = actual yield/ calculated yield x 100
- Reasons why percentage yield is less than 100%: not all reactants react fully, some reactants left in container, some products escsape.
- Atom economy = (Mr of desired product/ Mr of all products) x 100
- Reasons why atom economy is less than 100%: too many products.
- Importance of high atom economy: saves money, less waste products, saves energy, better for the environment.