- Q = It
- Q: charge (C)
- I: current (A)
- t: time (s)
- Current is the rate of flow of charge.
- Charge is a property of all matter and that there are positive and negative charges.
- Static electricity is produced when two surfaces rub. One surface gains electrons and becomes negatively charged, and the other loses electrons and becomes positively charged.
- P3.1c
- P3.1d
- Charged objects exert non-contact forces of attraction or repulsion on one another.
- For charge to flow, we need: a source of potential difference in a closed circuit.
- Series Circuits: (one loop). Current is the same everywhere. Voltage adds up to battery. Resistance adds up.
- Parallel Circuits: Voltage is the same everywhere. Current adds up from each branch.
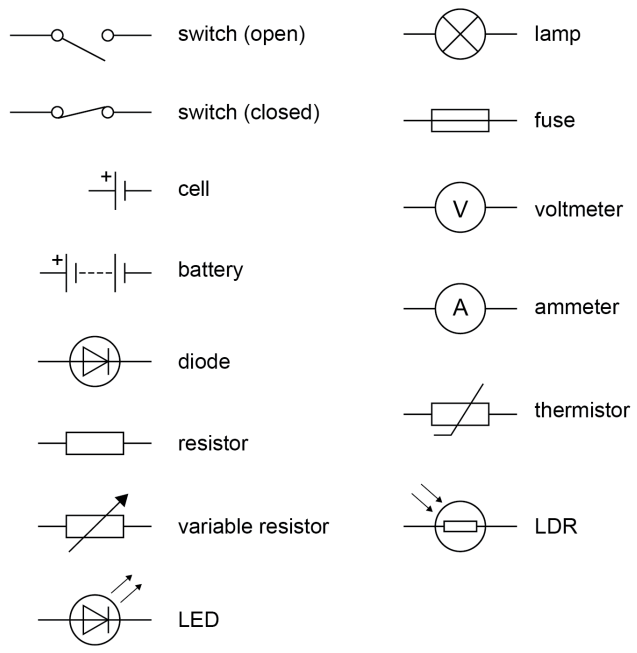
- Cells: provide voltage. Pushes charge
- Batteries: two or more cells.
- Open switch: off
- Closed switch: on (connected)
- Resistor: controls current to a certain level.
- Variable Resistor: this can be adjusted manually.
- Diode: only allows current to flow in one direction (high resistance backwards).
- Ammeter: measures current (connect in series).
- Voltmeter: measures potential difference (connect in parallel).
- Thermistor: as temperature increases, resistance decreases automatically (thermostats)
- LDR: as light intensity increases, resistance decreases automatically (street lamps).
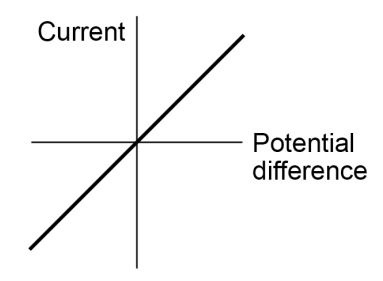
- In a fixed resistor, resistance is constant, which is shown by the straight line.
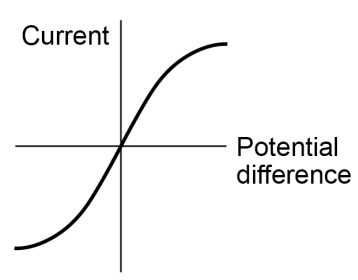
- In a filament lamp, as current increases, electrons collide with each other, so temperature increases, so resistance increases, so current stops increasing.
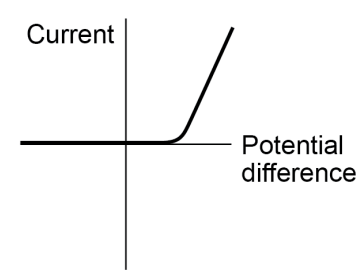
- In a diode, current cannot change direction so the I-V graph doesn't go down.
- If two resistors are in series, the total resistance adds up.
- If two resistors are in parallel, the total resistance is decreased and total resistance is lower than the value of the weakest resistor.
- V = IR
- V: potential difference (V), I: current (A), R: resistance (Ω)
- P = IV
- P = I2R
- E = Pt
- E = QV
- P: Power (W), E: Energy (J)